Images are the silent superstars of the web. They catch the eye, break up text, and bring your content to life. But beyond just making a page look pretty, images can play a strategic role in bringing organic traffic via search engines. When you optimize your images properly, search engines like Google can better understand them, index them, and show them in image search results — which can lead users right to your site.
 |
| How to Optimize Images for Organic Search Traffic? |
In this blog, we’ll walk through why image optimization matters, how search engines “see” images, and practical steps you can take to improve your site’s performance and visibility. The language is simple and clear so you can apply these ideas whether you’re a beginner or brushing up on best practices.
Why Optimizing Images Matters
Optimized images help your website in multiple ways:
Faster load times
When images are correctly sized and compressed, your pages load faster. Page speed is not just a convenience for users — it’s a ranking factor for search engines. Heavy, slow images can drag down your entire site’s performance and push visitors away before they even see your content. (Search Engine Watch)
Better visibility in search results
Search engines don’t “see” pictures the way humans do — they read text. If you don’t tell them what the image contains or why it’s relevant, they may ignore it. But when you add text that clearly describes your visuals, Google and others can index your images and show them in image search listings. That means more organic traffic from people searching for pictures, not just text. (Similarweb)
Improved user experience
When your site loads quickly and looks good on all devices, visitors stay longer, engage more, and are more likely to share your content. A positive experience translates indirectly into better search rankings.
How Search Engines “Read” Images
Search engines use a few different signals to understand what an image is about:
Image file name
Search bots look at the name of your image file. Generic names like IMG_12345.jpg tell the search engine nothing. Descriptive filenames like organic-coffee-beans-packaging.jpg give real context. (SEO Design Lab)
Alt text (alternative text)
Alt text is a short string you write to describe the image. If the image doesn’t load, browsers show this text. It also helps visually impaired users via screen readers. Most importantly for SEO, alt text gives search engines direct clues about what’s in the picture. When written well, it can include keywords naturally without sounding awkward. (Social Roots)
Captions and surrounding text
Search engines also consider the text around an image to understand relevance. A picture placed within a well-written paragraph about a topic strengthens the connection between the image and the subject. (SEO Design Lab)
Structured data (optional advanced)
For certain types of content like products or recipes, using structured schema markup helps search engines understand more details about the image and display it in rich search results. (Social Roots)
Choose the Right Image Format
Not all image formats are created equal. The type you choose affects both quality and performance.
JPEG
Great for photos or complex visuals with lots of colors. It compresses well and keeps file size low. (Social Roots)
PNG
Good for simple graphics, logos, or images needing transparency. It preserves detail but can be heavier than JPEG. (Social Roots)
WebP and AVIF
Modern formats that keep quality high while shrinking file size dramatically. These formats are supported by most modern browsers and are becoming the go-to choice for performance-focused sites. (Imagify)
Using the right format can make your site load faster without sacrificing clarity. Speed, remember, boosts user experience and SEO performance.
Keep Image Sizes Under Control
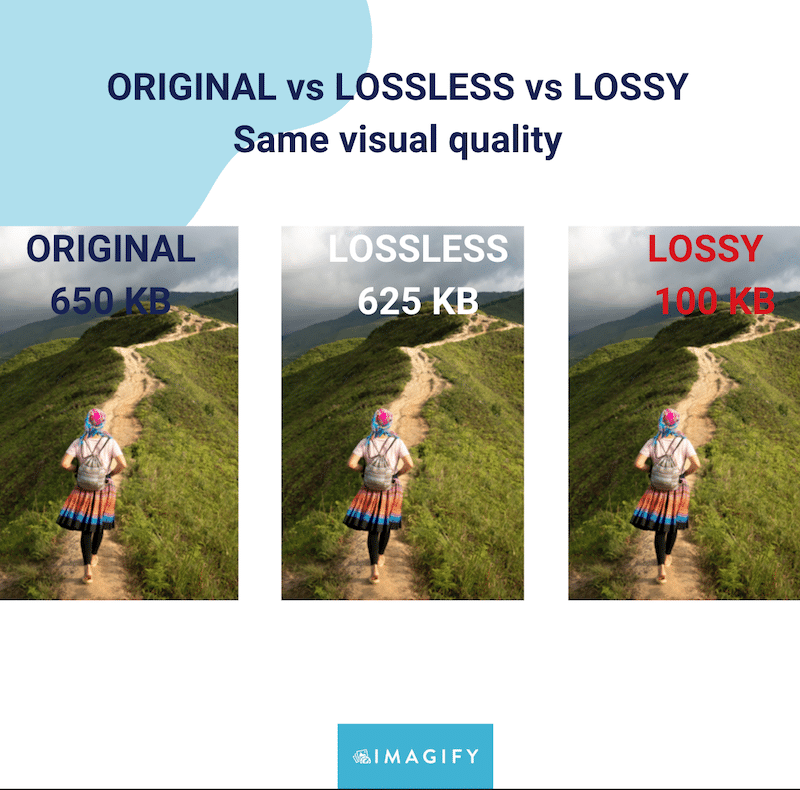
Large image files slow down your pages. Before uploading any image to your website, resize and compress it. You can do this manually with editing tools or with online compressors.
Resizing ensures the image dimensions fit the space where it will be shown. For example, a blog’s featured image might display at 1200 pixels wide, so uploading a 4000-pixel wide image is unnecessary. Compressing the file reduces its weight (in kilobytes) while keeping visual quality intact. (SEO Design Lab)
A good rule of thumb is to aim for file sizes under 200 kilobytes for most images and even smaller for tiny graphics. This helps your site load fast and makes search engines happier.
Write Useful Alt Text
Alt text isn’t about cramming keywords — it’s about describing what the image actually shows. Good alt text is brief, clear, and includes relevant keywords when it makes sense.
For example, if you have an image of a sunset over a beach, a description like “sunset over a tropical beach with palm trees” gives more context than “beach.” Keeping alt text under 125 characters ensures it’s fully read by screen readers and indexed correctly. (TechWyse Internet Marketing)
Alt text is also essential for accessibility. People who rely on screen readers will hear this description in place of the image, so treat it as a caption in words.
Use Descriptive File Names
When you save an image, name the file with real words that describe it. Search engines split words at hyphens (not underscores), so name your files like organic–travel–bag.jpg rather than IMG_9876.JPG. (Content Marketing Institute)
These filenames help both humans and search engines understand what the image contains, making it more likely to show up when someone searches for related terms.
Add Stable Dimensions
By specifying width and height attributes in your image HTML, you help browsers reserve the right amount of space while loading the page. Without these, images can shift the layout unexpectedly as the page renders, which hurts user experience and SEO metrics like Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). (Search Engine Journal)
Lazy Load Images
Lazy loading tells the browser to delay loading images until they’re about to appear on the screen. This speeds up initial page load, especially on long pages with many pictures. Most modern content management systems and web platforms support lazy loading natively. (Social Roots)
Lazy loading benefits mobile users and anyone on a slower connection because the browser doesn’t waste time downloading images that the visitor might never scroll to.
Make Images Mobile-Friendly
Today, more searches happen on phones than desktops. Responsive images adapt to different screen sizes so a small phone doesn’t have to load a giant desktop image. Using srcset in HTML allows the browser to choose the best image size for the device.
Mobile-friendly images not only improve appearance but also help with engagement metrics, which indirectly influence SEO. (Social Roots)
Use Unique Images When Possible
Stock photos are fine, but original images tell a different story. They set your content apart and give search engines fresh content to index. Unique visuals tied closely to your topic help boost relevance and user interest. (Content Marketing Institute)
Combine Images with Good Page Content
Images don’t stand alone. The text around them, including headers, paragraphs, and captions, reinforces their meaning. Search engines use this context to decide how relevant the image is to a user’s query.
So make sure the content and visuals complement each other. An image on “healthy recipes” should be surrounded by related text, not random unrelated material. (BrandCrowd)
Track Performance and Improve
Use tools like Google Search Console to see how your images perform in search. You can check which queries bring up your pictures and which pages generate the most impressions. If something isn’t working, revise the alt text, file names, or surrounding content to tighten relevance. (She Knows SEO)
Image optimization isn’t a one-and-done task. As your content grows or changes, revisit your images and keep them aligned with your SEO goals.
A Small Effort with Big Rewards
Optimizing images may feel like a detail, but it’s a low-effort, high-impact part of SEO. For many sites, improved image SEO leads to measurable gains in organic traffic, especially from Google Images and related search features. Sometimes just fixing alt text and compressing pictures can noticeably boost rankings. (Reddit)
Well-optimized images help your pages load faster, make your content more accessible, and give search engines richer information to index and serve to users. It’s a behind-the-scenes upgrade that delivers benefits on multiple fronts.
In Summary
If you want more organic search traffic from images, remember these core steps:
Choose the right image format and compress files. (Social Roots)
Write descriptive alt text that makes sense to humans and search engines. (TechWyse Internet Marketing)
Use meaningful file names instead of defaults. (Content Marketing Institute)
Make images mobile-friendly and fast-loading with responsive sizing and lazy load. (Social Roots)
Link images to strong page content and context. (BrandCrowd)
By treating images as part of your SEO strategy instead of an afterthought, you unlock a stream of organic visibility that many sites overlook.
Related Questions & Answers
How do optimized images help increase organic search traffic?
Optimized images improve page load speed, user experience, and accessibility, which are ranking factors for search engines. Proper file names, alt text, and compression help search engines understand images better, increasing visibility in Google Images and driving additional organic traffic to your website.
What role does image alt text play in organic image search?
Alt text describes an image’s content for search engines and screen readers. Well-written, keyword-relevant alt text helps images rank in image search results, improves accessibility, and provides context when images fail to load, indirectly supporting overall SEO performance.
Why is image file size important for SEO and traffic?
Large image files slow down page loading, negatively impacting user experience and Core Web Vitals. Faster-loading pages tend to rank higher in search results. Compressing images without quality loss improves performance, reduces bounce rates, and helps attract more organic search traffic.
How do image file names affect organic search visibility?
Descriptive image file names help search engines understand image content before crawling the page. Using relevant keywords instead of generic names like “IMG123.jpg” improves image indexing, increases chances of appearing in image search results, and supports better organic visibility.
Does image format impact organic search rankings?
Yes, modern image formats like WebP and AVIF offer smaller file sizes with high quality. Using these formats improves page speed and performance metrics. Better performance supports higher rankings, which can indirectly increase organic traffic from both image and web search.
How does image relevance affect organic traffic growth?
Relevant images aligned with page content improve user engagement and dwell time. Search engines interpret strong engagement signals as content quality indicators. When images match search intent and context, pages perform better in rankings and attract more consistent organic search traffic.
Can structured data improve image search traffic?
Structured data helps search engines better understand image context, especially for products, recipes, and articles. By adding schema markup, images can appear in rich results or enhanced listings, improving visibility, click-through rates, and organic traffic from image-based searches.
Why is mobile image optimization important for organic search?
Most image searches happen on mobile devices. Responsive images, proper sizing, and fast loading ensure a smooth mobile experience. Since mobile-first indexing is standard, optimized images help improve rankings and organic traffic from mobile search results.
How do image sitemaps help with organic image traffic?
Image sitemaps help search engines discover images that may not be easily found through crawling alone. Submitting image sitemaps improves indexing, increases visibility in image search results, and helps drive targeted organic traffic to image-heavy pages.
How does page context influence image ranking in organic search?
Search engines rank images based on surrounding text, headings, and overall page relevance. Images placed near relevant content with optimized captions perform better in search. Strong contextual alignment increases image ranking potential and contributes to higher organic search traffic.